Nutrition and Muscle Building - A Powerful Duo Against Sarcopenia!
With Nutrition and Strength Training for Better Quality of Life
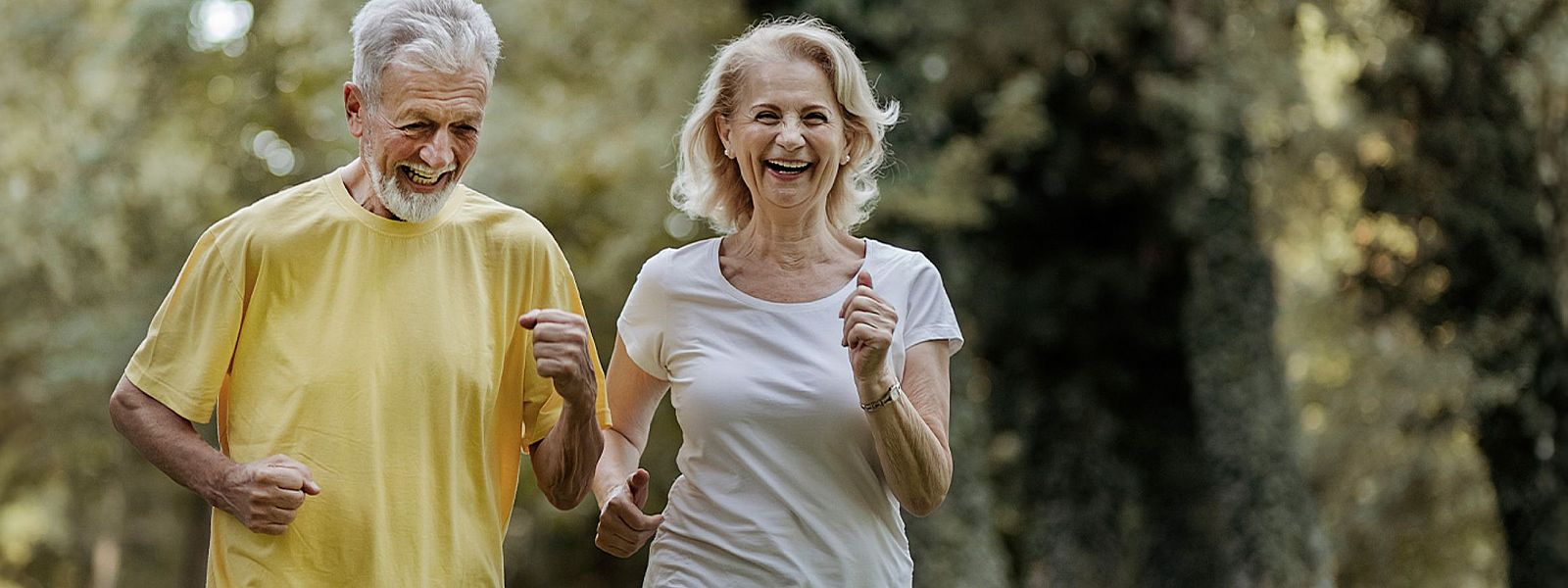
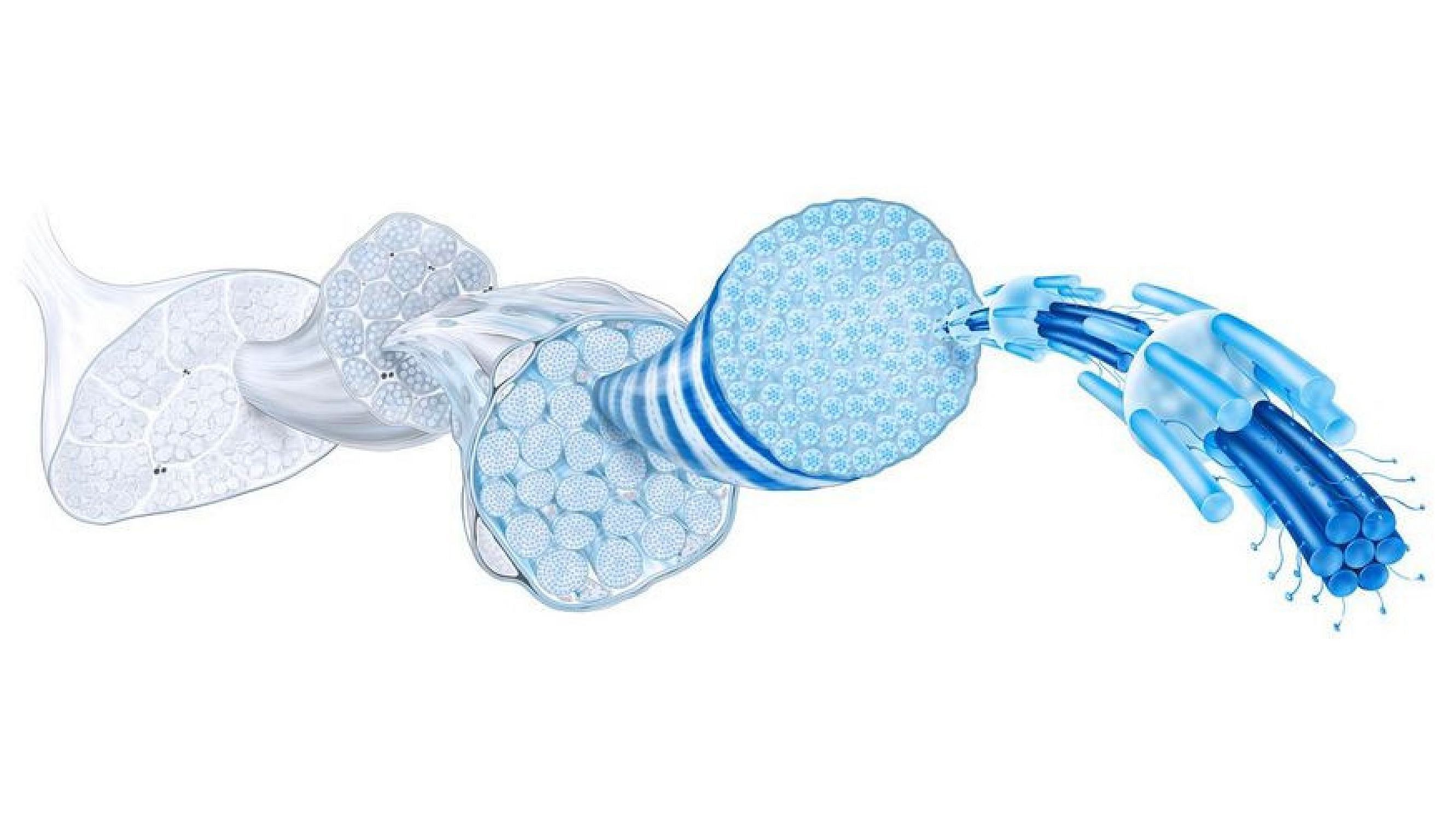
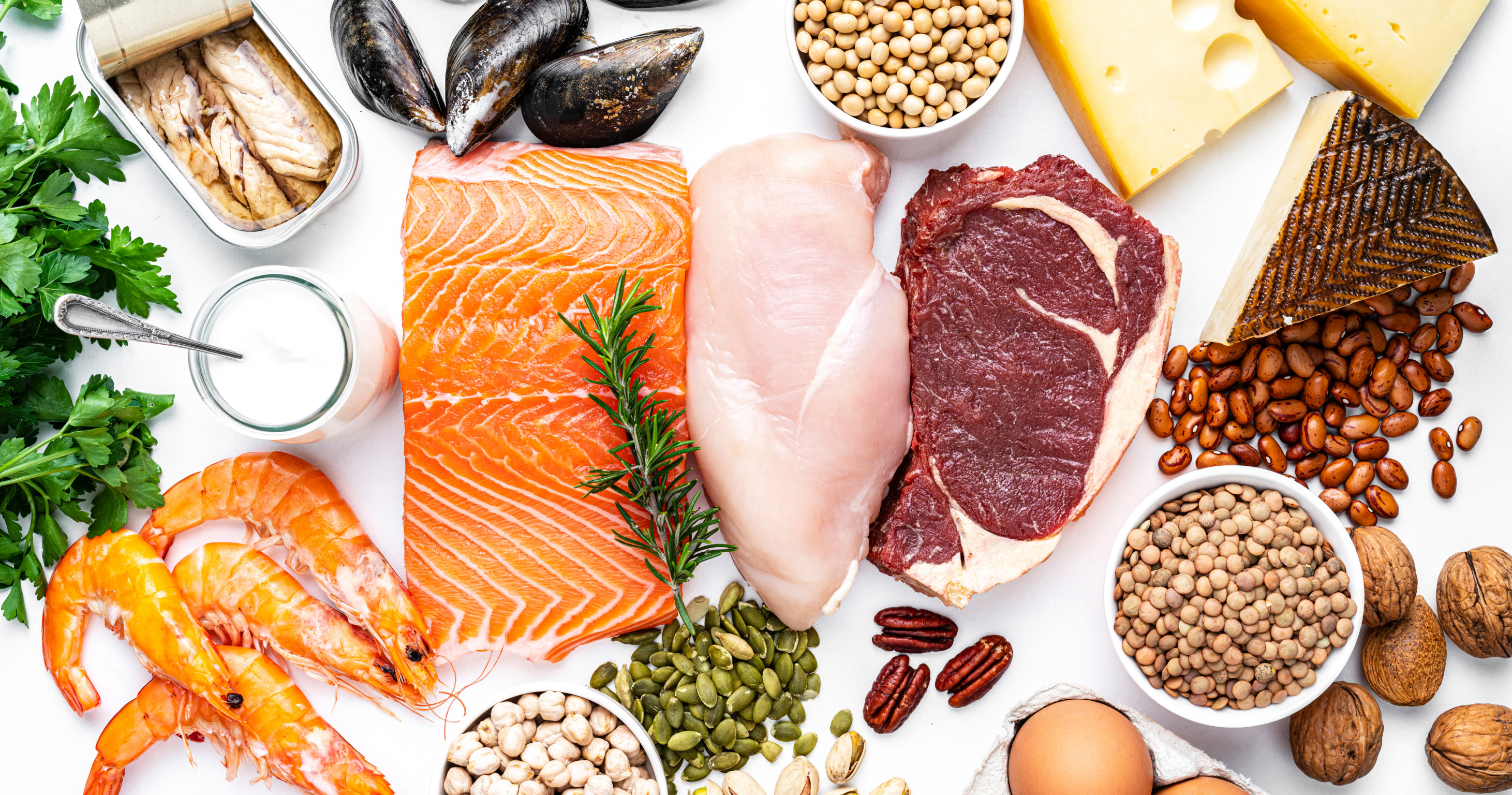
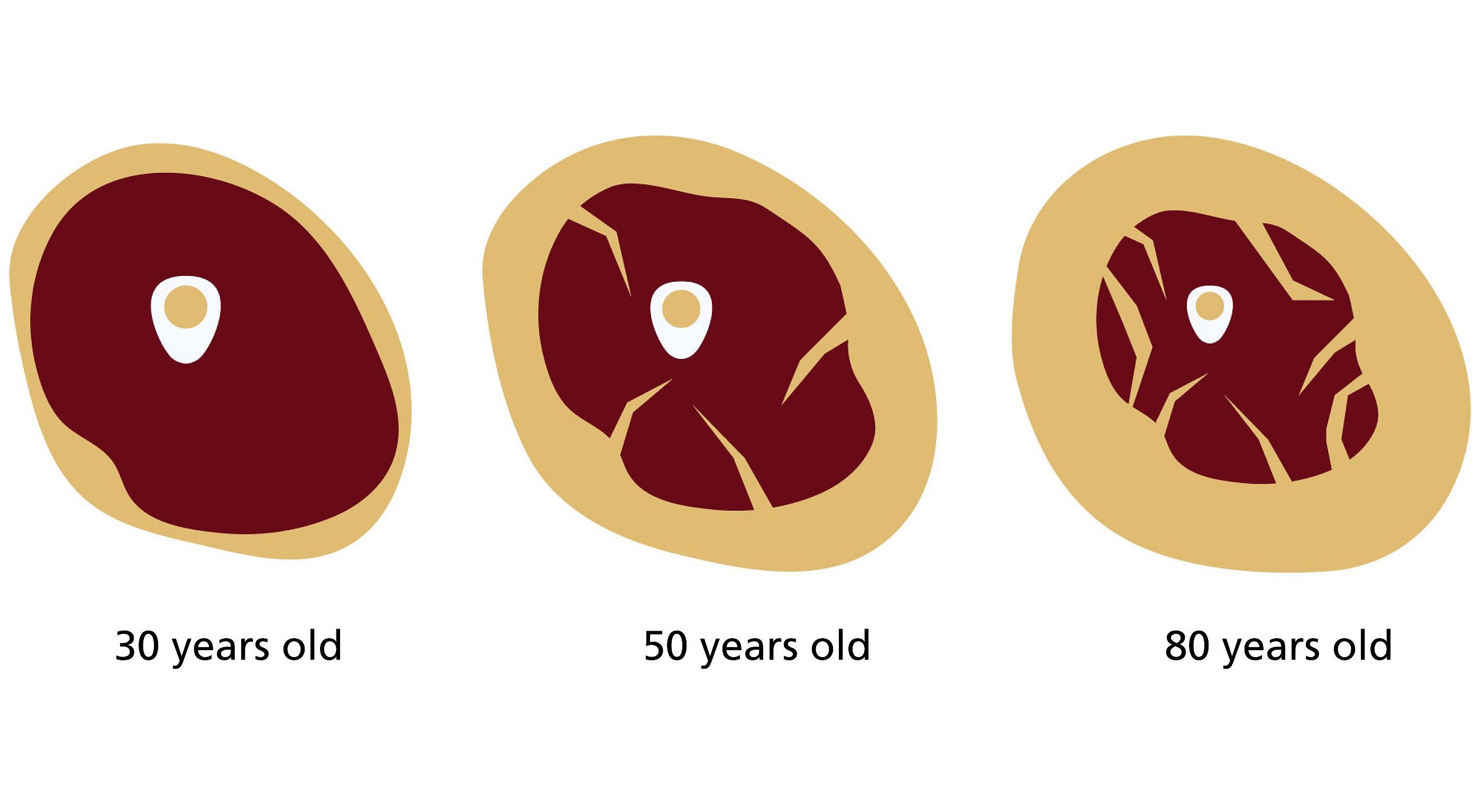
Muscle building and maintenance are a matter of proper nutrition and regular training. Both protein intake through food and continuous strength training are essential to maintain muscle function and prevent age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia). In this article we will show you how to strengthen your muscles and keep them healthy through the right nutrition and training strategy. For a better understanding, we explain the underlying biochemical processes and the medical importance of myokines. Learn more about the necessary amount of protein, suitable foods, effective training plans and other important preventive measures. This will help you stay active and independent into old age.